-
 Overview
Overview
Centre Testing International Group Co., Ltd. (CTI) is a market leader in testing, inspection, certification, calibration, audit, training & technical services; building trust between governments, enterprises, and consumers.
-
 Sustainability
Sustainability
By building a full value chain ESG governance system covering the strategic decision-making level, management execution level and business operation level, it actively practices penetrating management of ESG risk and opportunities, empowering sustainable development across the industry chain.
-
 Our service
Our serviceCentre Testing International Co., Ltd. (CTI) is the pioneer and leader in the TIC Industry which provides one-stop solutions on testing, inspection, certification, calibration, audit, training & technical services.
-
By Industry
Our service capabilties cover the upstream and downstream of the supply chain including textile and apparel,toys,electronic appliances,medical health,food...andother industries.
-
 Environment
Environment
-
 Raw Material & Fuel Chemicals
Raw Material & Fuel Chemicals
-
 Textiles, Apparel, Footwear & Accessories
Textiles, Apparel, Footwear & Accessories
-
 Food & Agricultural Products
Food & Agricultural Products
-
 Cosmetics, Personal Care & Household Chemicals
Cosmetics, Personal Care & Household Chemicals
-
 Building Materials&Construction Engineering
Building Materials&Construction Engineering
-
 Electronic & Electrical Appliances
Electronic & Electrical Appliances
-
 Toys, Furniture & Home Decoration
Toys, Furniture & Home Decoration
-
 Industrial Equipment & Manufacturing
Industrial Equipment & Manufacturing
-
 Rail & Aviation
Rail & Aviation
-
 Automotive & Spare Parts
Automotive & Spare Parts
-
 Pharma and Medical Services
Pharma and Medical Services
-
 Maritime Vessel Compliance Testing
Maritime Vessel Compliance Testing
 By Industry
By IndustryOur service capabilties cover the upstream and downstream of the supply chain including textile and apparel,toys,electronic appliances,medical health,food...andother industries.
-
-
 Specialty
SpecialtyComprehensively guarantee quality and safety, promote compliance and innovation, demonstrate brand competitiveness, and achieve higher quality, healthier, safer, and greener sustainable development.
-
 Management
ManagementWe have established a clear governance structure in accordance with listing requirements and national regulations and policies to deal with internal and external challenges and achieve sustainable development.
-
 Information DisclosureWe are committed to establishing normal and effective two-way communication with shareholders and investors. We have established a complete information disclosure mechanism to convey information to shareholders in a timely manner.
Information DisclosureWe are committed to establishing normal and effective two-way communication with shareholders and investors. We have established a complete information disclosure mechanism to convey information to shareholders in a timely manner.
-
 Talents Policy
Talents PolicyEnsuring the basic rights and benefits of employees;
Providing professional skills training to promote employees’ growth;
Carrying out various kinds of activities to balance employees’ work and life.
-
 RecruitmentWelcome to join CTI family! We are providing a platform for you to show your talents and achieve your career aspiration.
RecruitmentWelcome to join CTI family! We are providing a platform for you to show your talents and achieve your career aspiration.
Batteries and accumulators placed on the markets of EU member states need to meet the requirements of the EU Battery Directive, and those placed in China and the United States also need to meet GB 24427-2021 Content limitation of mercury, cadmium and lead for zinc anode primary battery and Public Law 104-142 Mercury-Containing and Rechargeable Battery Management Act. CTI Centre Testing International can provide testing of substances controlled by the EU Battery Directive, material risk analysis, corporate hazardous substance control recommendations and customized environmental protection programs.

◉ Business challenges
What hazardous substances do batteries need to be controlled?
How to deal with battery labeling requirements?
◉ Service Background
Batteries may contain mercury, lead, cadmium, other heavy metals and acid or alkali electrolyte solutions. If they are not properly handled, they will cause varying degrees of harm to the human body and the ecological environment. Therefore, the collection and post-processing of used batteries are very important. The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union issued Directive 2006/66/EC about Batteries and Accumulators and Waste Batteries on September 26, 2006. The Directive relates to the restrictions of hazardous substances in batteries, and the relevant policies for the recycling and recycling of used batteries. On December 10, 2013, the European Union announced the revised directive 2013/56/EU of 2006/66/EC. The new battery directive revised several exemptions. The EU battery directive includes battery hazardous substances limit requirements, labeling requirements and recycling rate requirements.
On April 30, 2021, the State Administration for Market Regulation and the Standardization Administration of China issued the national mandatory standard GB 24427-2021 Content limitation of mercury, cadmium and lead for zinc anode primary battery, which replaced GB 24427-2009 Limitation of mercury, cadmium and lead contents for alkaline and non-alkaline zinc manganese dioxide batteries and GB 24428-2009 Limitation of mercury content for zinc silver oxide, zinc oxygen and zinc manganese dioxide button batteries. The new standard will be officially implemented on November 1, 2021.
In 1996, the United States promulgated the Public Law 104-142: Mercury-Containing and Rechargeable Battery Management Act, which came into effect on May 13, 1996, requiring battery manufacturers to use a uniform prescribed label. Detailed regulations have also been made on the transportation, collection and storage of batteries and waste batteries, and manufacturers are encouraged to invest in battery recycling and proper disposal of waste batteries, and to encourage research and production of new batteries.
◉ Service content
1. Applicable product range
All types of batteries and accumulators, regardless of their shape, volume, weight, material composition and scope of use.
2. Routine sample requirements
Please contact our business or customer service, subject to specific standards.
3. Testing standards/evaluation standards
2006/66/EC, 2013/56/EU, GB 24427-2021,GB/T 20155,Public Law 104-142
4. control projects
EU Battery Directive:
Member States shall prohibit the placing on the market of:
(a) all batteries or accumulators, whether or not incorporated into appliances, that contain more than 0,0005 % of mercury by weight; and
(b) portable batteries or accumulators, including those incorporated into appliances, that contain more than 0,002 % of cadmium by weight.
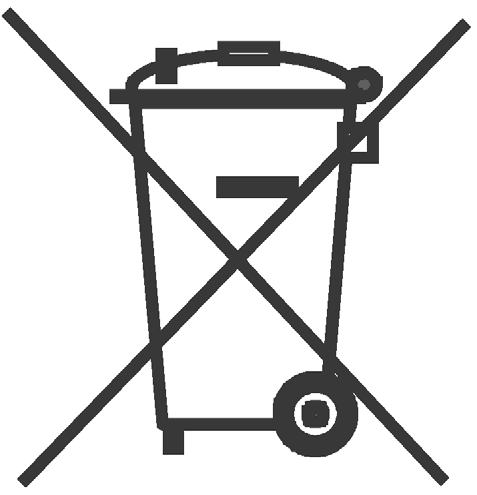
Member States shall ensure that all batteries, accumulators and battery packs are appropriately marked with the symbol
Batteries, accumulators and button cells containing more than 0,0005 % mercury, more than 0,002 % cadmium or more than 0,004 % lead, shall be marked with the chemical symbol for the metal concerned: Hg, Cd or Pb. The symbol indicating the heavy metal content shall be printed beneath the symbol indicating ‘separate collection’ for all batteries and accumulators shall be the crossed-out wheeled bin and shall cover an area of at least one-quarter the size of that symbol.
China battery mandatory standard:
|
The battery type |
Mercury content(μg/g) |
Cadmium content(μg/g) |
Lead content(μg/g) |
|
zinc silver oxide button batteries |
≤5 |
≤40 |
≤200 |
|
alkaline zinc oxygen button batteries |
≤5 |
≤40 |
≤500 |
|
alkaline zinc manganese dioxide button batteries |
≤5 |
≤20 |
≤40 |
|
non-alkaline zinc manganese dioxide batteries |
≤1 |
≤100 |
≤1000 |
|
alkaline zinc manganese dioxide batteries |
≤1 |
≤10 |
≤40 |
|
Note: Refer to Table 1 for the specific battery models that have been standardized, and see Appendix A for the comparison of the size codes of the new and old models of button batteries. Other unstandardized zinc silver oxide, zinc oxygen, zinc manganese dioxide button batteries shall be implemented according to the requirements in this table. |
|||
According to the labeling requirements in GB/T 8897.1; Hazardous substances can be marked as "mercury-free", "cadmium-free" and "lead-free" according to the content of mercury, cadmium and lead.
US battery requirements:
|
alkaline-manganese battery containing mercury
|
forbidden |
|
alkaline-manganese button cells containing mercury
|
≤25 milligrams of mercury per button cell
|
|
zinc-carbon battery containing mercury
|
forbidden |
|
button cell mercuric-oxide battery
|
forbidden |
|
other mercuric-oxide battery |
the battery manufacturer or importer clearly identifies the battery collection site |
Battery manufacturers must use the uniformly prescribed repeating cycle symbol for the marking of batteries and battery packs. Different types of batteries must also be marked with different words, such as lead-acid batteries, must have the words "Pb" or "LEAD", "RETURN", "RECYCLE", and if the regulated battery is sealed, it must also have the words “BATTERY MUST BE RECYCLED”.

◉ Solution
Testing of battery directives and controlled substances
Risk assessment of materials
SDS preparation of raw materials
Evaluation of battery recovery rate
Battery symbol evaluation
Internal and supplier management training consulting services On-site audit of the management and control of hazardous substances in the battery of the company or the supplier
◉ Our strengths
CTI Group has many advanced equipment and has passed CMA/CNAS qualification accreditation, the test data is accurate and reliable, and the test report has international credibility.
The scientific laboratory information management system ensures the efficient operation of each service link.
The technical expert team has rich practical experience and can provide professional, rapid and comprehensive one-stop service.
The service network is all over the world, and many first-line brands designate cooperative laboratories.
◉ Service Process
Consult customer service → confirm test plan → fill in application form → send samples → pay test fees → test → send reports and invoices
◉ Frequently asked questions
1. How long does the test take?
Normal 4 working days. If you need faster, please contact our business or customer service.
2. Whether the content limit of hazardous substances in batteries is based on homogeneous material evaluation or article evaluation?
According to the entire battery evaluation, conventional battery products are divided into homogeneous material tests, and the test results are converted into the content of finished battery products.
3. If the battery test is RoHS2.0 qualified, is the battery directive also qualified?
Not necessarily, the EU RoHS2.0 control scope does not include batteries, and the EU RoHS2.0 test of electronic products needs to remove the battery. The substance limit controlled by the battery directive is lower than that of RoHS. Even if RoHS2.0 is qualified, the battery directive may not be qualified.































 粤公网安备 44030602000441号
粤公网安备 44030602000441号